Why cord blood donation is important? These ‘hematopoietic stem cells’ have capability to generate new blood cells. Image Courtesy – https://financialtribune.com. Image Courtesy – Business Insider
‘Cord Blood’ – this medical term is quite common in modern treatment and research. The full term is ‘Umbilical Cord Blood’ or ‘Placental Blood’.
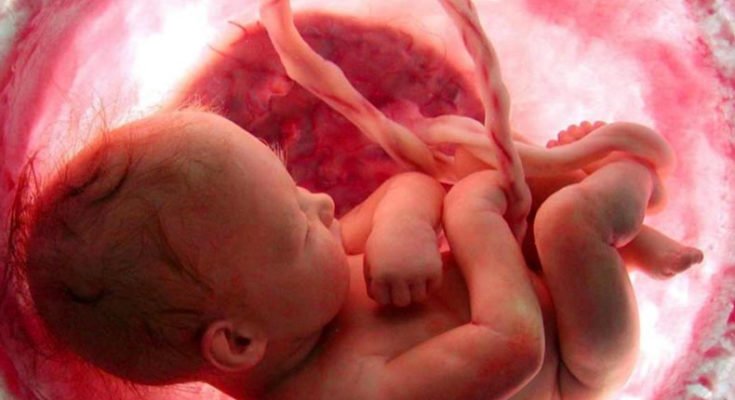
The umbilical cord is cut after a baby is born, but some amount of blood remains in the blood vessels of the placenta and also in the section of the umbilical cord that remains attached to it. This blood is called ‘umbilical cord blood’. It contains red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles, platelets and plasma as usual, but it has a specific property other than the normal blood, like ‘Hematopoietic Stem Cells’. These ‘hematopoietic stem cells’ have the capability to generate new blood cells.
Usage of this type of blood is increasing due to its potential source of stem cells. It is mostly used as a substitute for bone marrow for the treatment of leukaemia patients. This blood is also used in genetic diseases or metabolic diseases; apart from this, more than 80 different diseases are treated with this element presently.
According to the New York Blood Centre (NYBC), some of the diseases are diagnosed for transplantation of cord blood:
Leukemia –
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia
Acute Biphenotypic Leukaemia
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia
Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukaemia
Juvenile Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia
Juvenile Monomyelocytic Leukaemia
Leukaemia, Unspecified
Lymphomas –
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Disease
Epstein-Barr Virus / Lymphoproliferative Disease
Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Disease
Lymphoma, unspecified
Myelodysplasias –
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Myelofibrosis
Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes –
Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia
Diamond-Blackfan Anemia
Dyskeratosis Congenita
Fanconi’s Anaemia
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Reticular Dysgenesis
Severe Aplastic Anemia, Unspecified
Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome
Sideroblastic Anemia
Hemoglobinopathies –
Sickle Cell Disease
Thalassemia
Immune Deficiencies –
Common Variable Immune Deficiency
Congenital Immune Deficiency
DiGeorge syndrome
Griscelli Syndrome
Lymphocyte Adhesion Disease
Nezelof Syndrome
Omenn Syndrome
Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID)
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
X-linked Hyper-IgM Syndrome
X-linked Immune Dysregulation Polyendocrine Enteropathy
Histiocytosis –
Familial Erythrophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Hemophagocytic Syndrome
Histiocytosis
Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (Histiocytosis-X)
X-Linked Lymphoproliferative Disease
Read: Mosquito Bites may be a Gene factor
Metabolic Diseases –
MPS, not specified
Hurler Disease (MPS type IH)
Hurler-Scheie Disease (MPS type IS)
Hunter’s Syndrome (MPS type II)
Sanfilippo Disease (MPS type III)
Morquio Syndrome (MPS type IV)
Maroteaux-Lamy Syndrome (MPS type VI)
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Alpha-mannosidosis
Amyloidosis
Aspartylglucosaminuria
Austin’s Disease (Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency)
Fucosidosis
Gangliosidosis
Gaucher’s Disease
I-cell Disease (Inclusion Cell Disease)
Infantile Ceroid Lipofucoscinosis
Krabbe Disease
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
Neiman-Pick Disease
Osteopetrosis
Sandhoff Disease
Sialidosis
Tay Sach Disease
Wolman Disease
Neutrophil Disorders –
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)
Congenital Neutropenia
Kostmann Syndrome
Platelet Disorders –
Congenital Thrombocytopenia
Glanzmann’s Thrombasthenia
Other Malignancies –
Breast Cancer
Multiple Myeloma (Plasma Cell Disorder)
Neuroblastoma
Other Malignancy
Autoimmune diseases –
Systemic Lupus (SLE)
Other diseases –
Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria
Epidermolysis Bullosa
Process of cord blood preservation:
In the USA, there are numerous cord blood banks that provide several patients these essential stem cells. A mother has to sign an informed consent for donating the umbilical cord of her baby. This consent gives permission to the public blood banks to collect the cord blood after birth, and to register it on their database so that doctors can search on behalf of their patients. It is generally registered by its ‘genetic type’, and no information about the identity of the donor is registered.
Read: New technology for tooth rejuvenation will come very soon
A nationwide network of public blood banks is maintained with the donation registry record. In the USA, the registry of donors is called ‘Be The Match’. These records are linked up with the blood banks all over the world so that patients from any country can benefit.
Previously, the concept of cord blood banking was not very familiar to the people of India. But it is getting popular now. There are 2 types of banking facilities in India – Public donor banks and Private banks.
In the public donor banks, parents donate the cord blood of their baby to a central blood bank for the use of anybody who needs it. The cord is not stored specifically for a particular person or family member.
Once umbilical cord blood has been donated to a public bank, an individual no longer owns it. But if a member of your family needs it, the registries will be searched for the most appropriate match. This could be the one you donated if it has not already been used for another patient.
On the other hand, the private cord blood banking centres are built around the possibility of use; either by the same child at a later date or by siblings or a family member. Due to this reason, some people term it to be a form of ‘biological insurance’.
Collecting and storing cord blood at private banks in India is rather costly. Maybe some doctors have a vested interest or have financial benefits with private cord blood banks. The private cord blood banks also guarantee for perfect match with stored stem cells for future use.
But, in the USA, this type of blood donation is completely safe, and no collection charge or storage charge is taken in public cord blood banks. The cord blood of your baby gets registered with ‘Be The Match Registry’ in the USA as per the Stem Cell Therapeutic Reauthorization Act of 2010 and 2015.
Reference: DIAGNOSIS for Transplantation with NYBC CB units – list of diseases, National Cord Blood Program, Cryolife, Be The Match, etc.